PEMDAS Meaning: What is PEMDAS, How is it Used, and Is It Reliable?
A Post By: Anthony Persico
In mathematics, there is something called the order of operations, which is a rule for solving math problems that have more than one operation (adding, subtracting, multiplying, etc.). When studying math and learning how to correctly use the order of operations, many people rely on a common mnemonic known as PEMDAS as a memory aid for remembering the order of operations.
PEMDAS Meaning:
P=Parenthesis
E=Exponents
M=Multiplication
D=Division
A=Addition
S=Subtraction
These operations are meant to be performed from left to right, where the left-most operation is performed first. But this is only a general rule for remembering the order of operations and there are key nuances to the relationship between multiplication/division and addition/subtraction that must be remembered in addition to the mnemonic, PEMDAS, otherwise, it becomes a very unreliable tool that will often lead to getting wrong answers to seemingly math problems. These key nuances are highlighted in the sample section below.
PEMDAS Meaning: Key Ideas
PEMDAS has been around for a long time and many math students learn the phrase “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally” as a trick to remembering the order of operations in math.
However, PEMDAS is not a perfect mnemonic for remembering how to correctly perform the order of operations, but it can be a useful tool proved that you remember a few extremely important nuances:
Always perform parenthesis and/or groups first
After parenthesis and groupings, perform exponents
After parenthesis and exponents, perform multiplication/division (whichever comes first moving from left to right)
After multiplication/division, perform addition and/or subtraction (whichever comes first moving from left to right)
PEMDAS Meaning: Examples
It is one thing to remember the order of operations, and a completely task to know how to use it to solve math problems correctly. In fact, many old-timers can easily recall the phrase “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally” decades after grade school, but have no idea what the PEMDAS meaning is or how to use it properly.
Again, PEMDAS is only useful as a mnemonic if you also remember the previously mentioned key ideas and nuances. Now, let’s look at a few examples of how to correctly use PEMDAS to perform the order of operations.
PEMDAS Example 01: (3+1) x 4
Solve what is inside the parentheses first. In this case, 3+1=4.
Then perform multiplication: 4 x 4 = 16
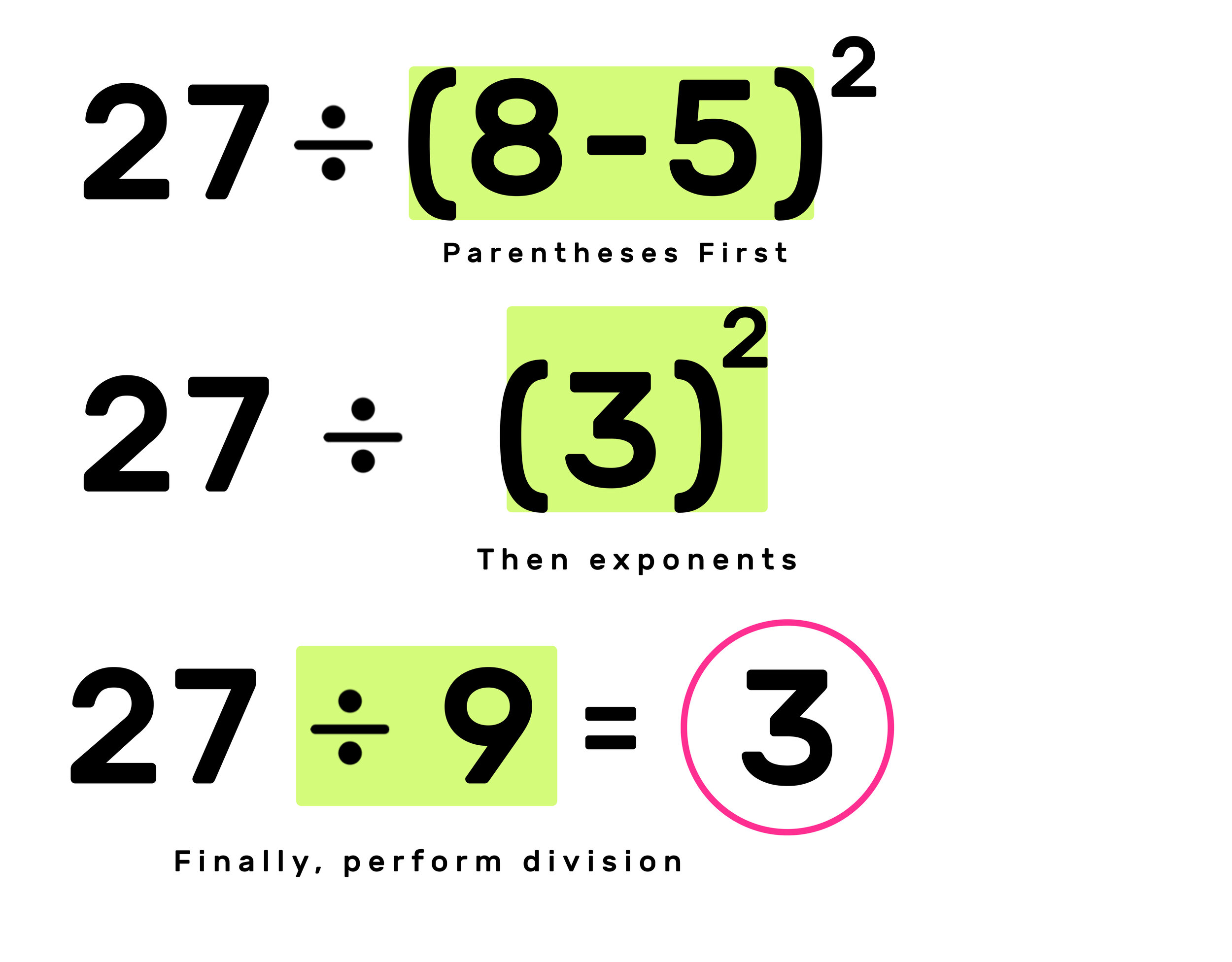
PEMDAS Example 02: 27 ÷ (8-5)^2
Just like the last example, solve what is inside the parentheses first. In this case, 8-5 = 3.
Then move onto the exponents 3^2=9. Finally, 27÷3 = 9
PEMDAS Example 03: 10 x 6 + 1
For starters, when there are no parentheses/groupings and/or exponents, you can skip the P and the E of PEMDAS.
According to PEMDAS, you have to perform multiplication/division before addition/subtraction, so you can go ahead and solve this problem from left to right:
10x6 = 60 and 60 + 1 = 61
PEMDAS Example 04: 75 - 10 x 5
Again, PEMDAS requires you to perform multiplication/division before addition/subtraction, so, in this example; you do not perform operations from left to right.
In this case, first perform 10 x 5 = 50, and then perform 75 – 50 = 25.
PEMDAS Example 05: 8 x 8 ÷ 16
This example highlights where the key nuances to PEMDAS make a huge difference. Remember that PEMDAS requires you to solve Multiplication/Division from left to right based on whichever comes first.
In this example, when moving from left to right, multiplication comes first so you would first perform 8 x 8 = 64.
Next, you would perform the division: 64 ÷ 16 = 4
Note: If you strictly followed PEMDAS moving from left to right in this example, you would have ended up with the correct answer, but let’s take a look at an example when division comes first, and multiplication comes second.
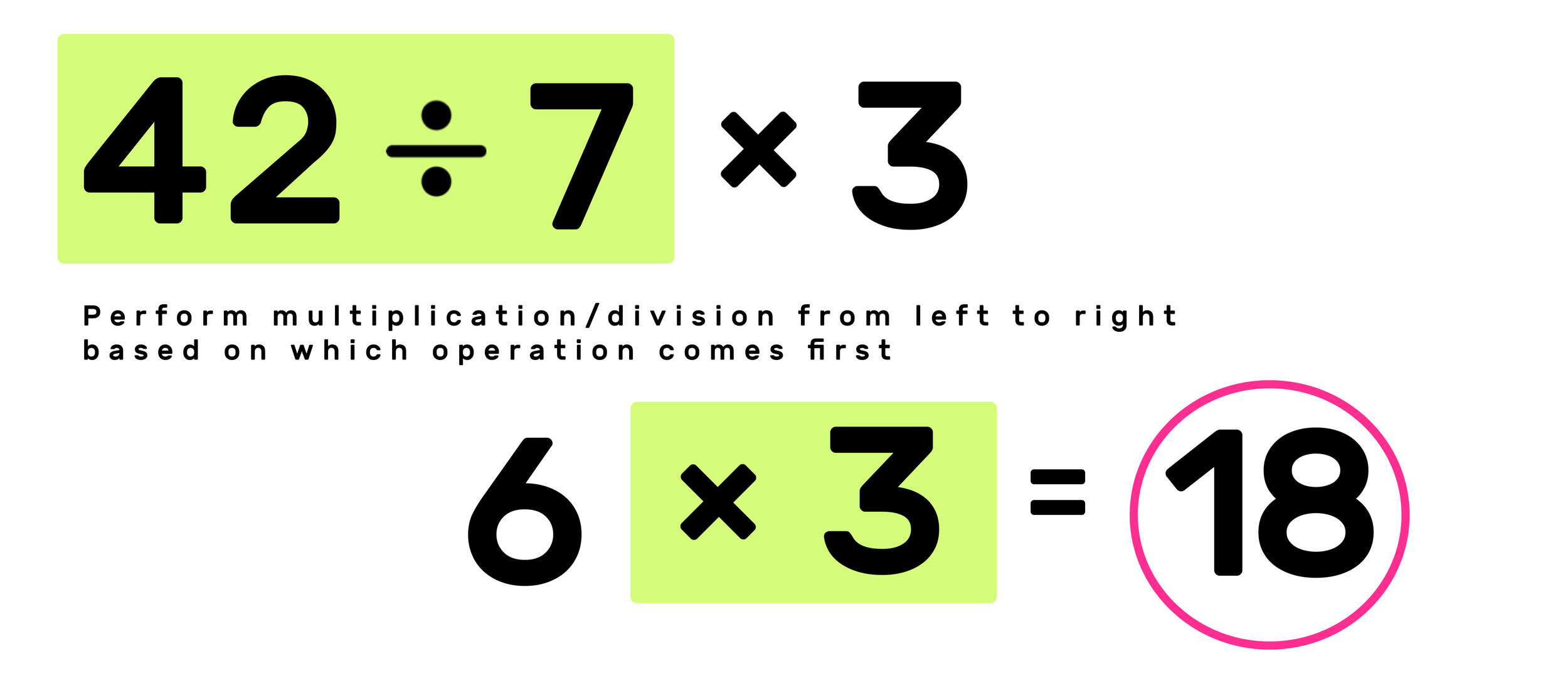
PEMDAS Example 06: 42 ÷ 7 x 3
In order to solve this problem correctly, you have to remember that a key nuance of the PEMDAS meaning is that you perform multiplication/division and addition/subtraction based on which operation comes first left to right.
Just because M (Multiplication) comes before D (Division) in PEMDAS, doesn’t mean that you always perform multiplication first.
In this example, notice that the only two operations are division and multiplication. Unlike the last example, division comes first this time, so you have to perform 42÷7=6 first and then 6x3=18 second.
Note: Many students fail to use PEMDAS correctly in these kinds of examples and perform multiplication first 42 / 21 = 2. Note that 2 is not the correct answer.
PEMDAS Meaning: Why Is It Important
Correctly applying the order of operations and using PEMDAS has become very popular in recent years due to viral math problems that pop up on social media. These kinds of posts are popular because individuals assume that the correct way to apply the order of operations is to perform each operation from left to right. Since most people get these seemingly simple math problems incorrect, they are encouraged to comment and share, which rapidly spreads the post in a viral nature.
However, if individuals could remember (A) the order of operations using a mnemonic like PEMDAS (or an even more useful one known as GEMS) and (B) the nuances to correctly applying the order of operations (namely the relationship between multiplication/division and addition/subtraction), then these kinds of viral problems could be easily solved without much controversy.
PEMDAS Meaning: Conclusion
PEMDAS is a prevalent, yet only somewhat useful mnemonic for remembering the order of operations in math. PEMDAS refers to the order of operations as follows: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction. While many individuals remember PEMDAS using the famous phrase “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally,” they often forget the important nuance that multiplication is not automatically performed before division and addition is not automatically performed before subtraction (multiplication/division and addition/subtraction are performed from left to right based on whichever operation comes first). This common misunderstanding devalues PEMDAS as a reliable memory tool and is the root cause of seemingly simple math problems going viral on social media because a large percentage of adults can remember the mnemonic decades after grade school, but can not get a correct answer.
PEMDAS has persisted as a go-to strategy for remembering the order of operations more because of nostalgia and resistance to change rather than it being the most effective strategy. And while using mnemonics is rarely a good strategy for understanding math concepts and developing reasoning skills, there are much better alternatives to PEMDAS, including GEMS, that are significantly more reliable.
Are you looking for a more effective and easier alternative to relying on PEMDAS?
More Free Math Resources for Grades K-8: